
- #HOW CAN I FIND THE HOST ID FOR MAC HOW TO#
- #HOW CAN I FIND THE HOST ID FOR MAC FULL#
- #HOW CAN I FIND THE HOST ID FOR MAC ANDROID#
- #HOW CAN I FIND THE HOST ID FOR MAC MAC#
- #HOW CAN I FIND THE HOST ID FOR MAC WINDOWS#
This TCP stream has HTTP request headers as shown in Figure 8. Select the second frame, which is the first HTTP request to and follow the TCP stream as shown in Figure 7.įigure 7: Following the TCP stream for an HTTP request in the third pcap Open the pcap in Wireshark and filter on http.request and !(ssdp).
#HOW CAN I FIND THE HOST ID FOR MAC WINDOWS#
This pcap is from a Windows host using an internal IP address at 192.168.197. The third pcap for this tutorial, host-and-user-ID-pcap-03.pcap, is available here.
#HOW CAN I FIND THE HOST ID FOR MAC ANDROID#
If the HTTP traffic is from an Android device, you might also determine the manufacturer and model of the device. User-agent strings from headers in HTTP traffic can reveal the operating system. The frame details section also shows the hostname assigned to an IP address as shown in Figure 6.įigure 6: Frame details for NBNS traffic showing the hostname assigned to an IP address Device Models and Operating Systems from HTTP Traffic
#HOW CAN I FIND THE HOST ID FOR MAC MAC#
Select the first frame, and you can quickly correlate the IP address with a MAC address and hostname as shown in Figure 5.įigure 5: Correlating hostname with IP and MAC address using NBNS traffic Open the pcap in Wireshark and filter on nbns. This pcap is from a Windows host using an internal IP address at. The second pcap for this tutorial, host-and-user-ID-pcap-02.pcap, is available here. Fortunately, we can use NBNS traffic to identify hostnames for computers running Microsoft Windows or Apple hosts running MacOS. We can easily correlate the MAC address and IP address for any frame with 1 as shown in Figure 4.įigure 4: Correlating the MAC address with the IP address from any frame Host Information from NBNS Trafficĭepending on how frequently a DHCP lease is renewed, you might not have DHCP traffic in your pcap. Based on the hostname, this device is likely an iPad, but we cannot confirm solely on the hostname. In this case, the hostname for 1 is Rogers-iPad and the MAC address is 7c:6d:62:d2:e3:4f. Client Identifier details should reveal the MAC address assigned to 1, and Host Name details should reveal a hostname.įigure 2: Expanding Bootstrap Protocol line from a DHCP requestįigure 3: Finding the MAC address and hostname in a DHCP request Expand the lines for Client Identifier and Host Name as indicated in Figure 3. Go to the frame details section and expand the line for Bootstrap Protocol (Request) as shown in Figure 2. Select one of the frames that shows DHCP Request in the info column.

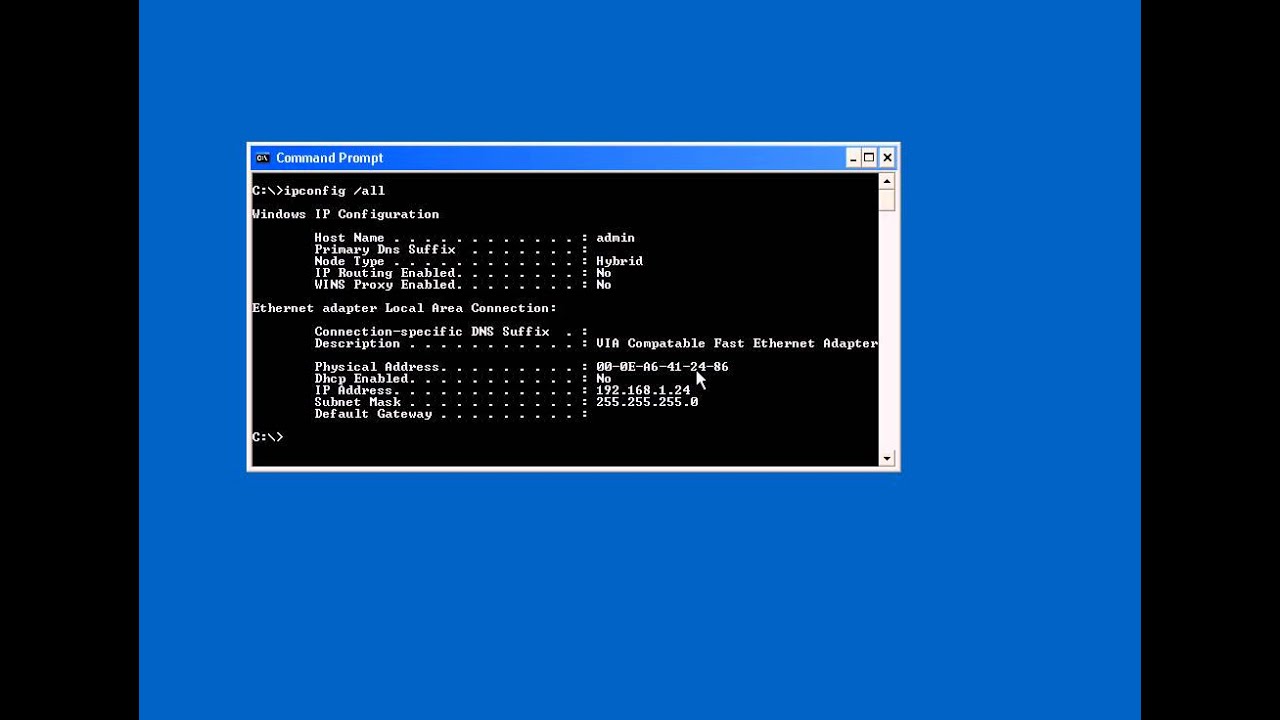
Note: With Wireshark 3.0, you must use the search term dhcp instead of bootp.įigure 1: Filtering on DHCP traffic in Wireshark This filter should reveal the DHCP traffic.

Open the pcap in Wireshark and filter on bootp as shown in Figure 1.
This pcap is for an internal IP address at 1. The first pcap for this tutorial, host-and-user-ID-pcap-01.pcap, is available here.
NBNS traffic is generated primarily by computers running Microsoft Windows or Apple hosts running MacOS. DHCP traffic can help identify hosts for almost any type of computer connected to your network. How do we find such host information using Wireshark? We filter on two types of activity: DHCP or NBNS.
#HOW CAN I FIND THE HOST ID FOR MAC FULL#
If you have access to full packet capture of your network traffic, a pcap retrieved on an internal IP address should reveal an associated MAC address and hostname. In most cases, alerts for suspicious activity are based on IP addresses.
#HOW CAN I FIND THE HOST ID FOR MAC HOW TO#
This tutorial offers tips on how to gather that pcap data using Wireshark, the widely used network protocol analysis tool. When a host is infected or otherwise compromised, security professionals need to quickly review packet captures (pcaps) of suspicious network traffic to identify affected hosts and users.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
